What is exactly the problem of universal health care systems? Why cannot economies maintain free health care for consecutive generations without struggling too much?
To the non-economist audience, it might sound reasonable for every country to execute and maintain a sustainable system that manages pensions, healthcare and other welfare payments uniquely and in one account, under ethical and practical standards that match their financing plans perfectly. Politicians bring this matter up during the debates before all the elections and according to the stage the country is in, voters decide whether the health care system must be empowered or weakened. But why a heavenly, ethical and sustainable public healthcare system does not exist for every country? In this article, I will try to avoid technical matters and focus on the outcomes of studies on the issue. In the first paragraph, I will attempt to go over some very basic economics, as known as Econ 101 and then, I will discuss the issue.
Specifically, we must consider the feasibility of welfare in every country. Well, some nations are wealthy, and some are not. Among wealthier nations, some of them are even wealthier and by some standards, they are getting more and more prosperous. To understand what I mean by wealth and being wealthy and getting wealthier, think of a simple quantified amount of wealth that each citizen holds. This wealth includes his/her financial assets, future income flows, savings, real estate and even knowledge. Taking an average of this value in dollars will easily help us rule out countries like China, India and Russia from wealthy countries and focus on the countries that have higher levels of what we refer to as “wealth per capita”. Without demonstrating many technical issues, the statistics of wealth show that a Chinese individual is not wealthier than an Eastern European citizen, of course on average.
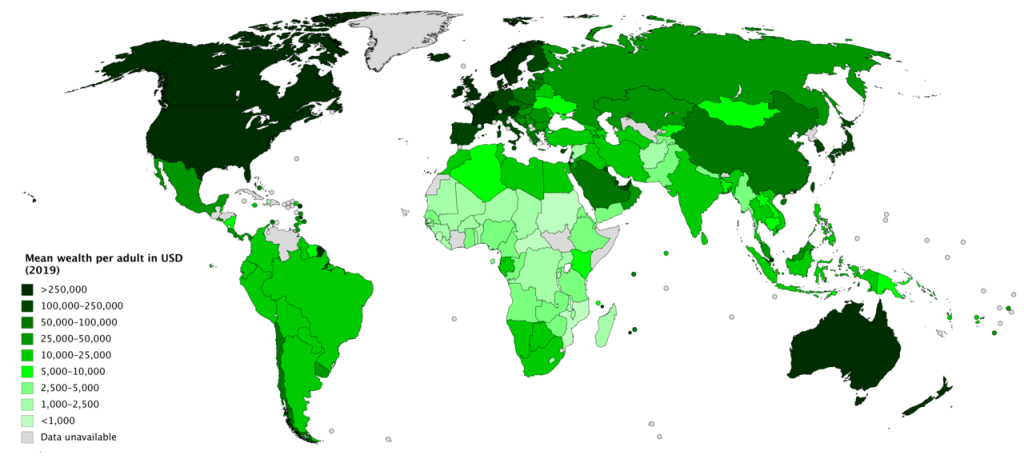
These wealthy nations in Western Europe, North America, Eastern Asia and Oceania are not easily capable of increasing welfare using a high marginal propensity of consumption rate. Instead, their idea has been to increase the number of years that each citizen lives. In simple words, people are getting enough from their normal life and giving them more does not satisfy them enough. Therefore, the allocation of the market tells the policymaker that it is tangible to invest in the length of life, rather than increasing welfare by increasing consumption at any point in time.
To conclude the previous paragraph that provided a simple overview, I refer back to the word feasibility: is the nation that is discussing a free healthcare system for everyone, “wealthy enough” to do so? I doubt that many nations are at this stage. Maybe few Northern European economies were capable of maintaining such healthcare systems for decades, but even in those countries, the natural ageing tendency of the society and higher life expectancy has brought an end to the infinite willingness to give everything to everyone for a relatively cheap price. Reconsiderations have started, and charging people for what they get is the most reasonable answer, just like the banana market. Pay 1 unit and get 1 banana, pay 2 and get two. In such markets, there are offers to receive more than you pay, when you pay more than average. Take the case of private retirement investment portfolios that insurance companies and banks offer to their clients.
Rather than feasibility, there is philosophical reasoning behind a private healthcare system, and it raises from a sort of moral hazard. Imagine healthy people start paying very high taxes for people that consume cigarettes or alcohol on a daily basis. What I mean is a public healthcare system, in which there is an annual fee paid as taxes or fees, and everyone pays the same amount! You may want to point out to almost every country that subsidizes negatively the consumer of smoking products by additional taxes. Simple algebra shows that the average amount a smoker pays through taxes does not cover the costs of one case of lung cancer in a public hospital.
Furthermore, some may mention that health is not an economic good that we shall consider like an ordinary product and therefore, the nature and characteristics of such “ethical” market must be different. So what is an economic good? Why isn’t lime or avocado subsidised to become available for the poorer classes in the society? This logic is misleading and calls for free education in universities, subsidised public transportation, subsidised fuel markets and at the end of the day, subsidises having children because it is “nice” and “ethical” to have children. This system is inefficient, works against its own standards by penalising citizens for every action in their daily lives and ends up in an inflationary economy that might even face a permanent stagnation.
Eventually, we have to think of COVID crisis as a heavy shock that hit our economies. The world will not be the same, welfare will decrease for some time and we have to pay for what we have not initiated, and it is far from being fair. The problem is there does not seem to be any other solution for such hard times. Calls for increasing public expenditures are nonsense and even dangerous. Take a look at the public debt crisis in Southern Europe and you will see what a true long-term disaster it can become.
